That’s the headline on my latest exclusive, out a few weeks ago.
It generated a lot of reader interest, and was picked up by several news outlets in India and the U.S.
It began: <-- 🎁 Gift link
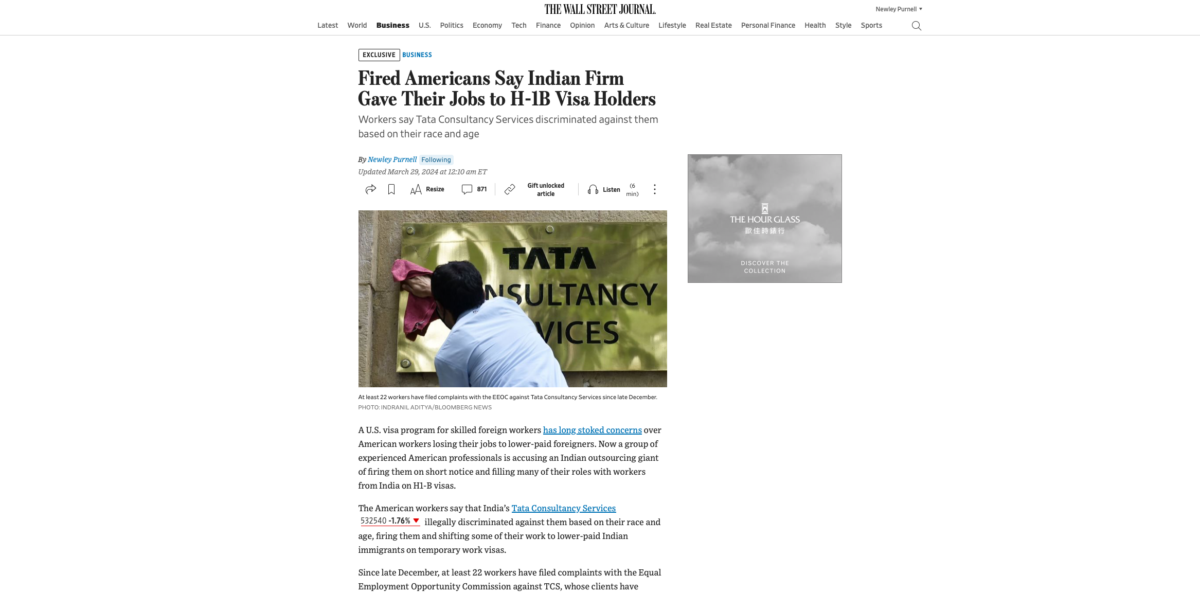
A U.S. visa program for skilled foreign workers has long stoked concerns over American workers losing their jobs to lower-paid foreigners. Now a group of experienced American professionals is accusing an Indian outsourcing giant of firing them on short notice and filling many of their roles with workers from India on H1-B visas.
The American workers say that India’s Tata Consultancy Services illegally discriminated against them based on their race and age, firing them and shifting some of their work to lower-paid Indian immigrants on temporary work visas.
Since late December, at least 22 workers have filed complaints with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission against TCS, whose clients have included dozens of the U.S.’s biggest companies.
The American former TCS employees are Caucasians, Asian-Americans and Hispanic Americans ranging in age from their 40s to their 60s and living in more than a dozen U.S. states. Many have master’s of business administration or other advanced degrees, according to the complaints, which were viewed by The Wall Street Journal.
While companies often conduct layoffs that affect workers with more seniority, the American professionals say TCS broke the law by targeting them based on protected characteristics of age and race. They say the company’s move demonstrated preferential treatment to Indian workers in the U.S. on the coveted visas.
A TCS spokeswoman said allegations that the company engages in unlawful discrimination are meritless and misleading. TCS has a strong record of being an equal opportunity employer in the U.S., acting with integrity in its operations, she said.
Click through to read the rest.